Arta CFD Laboratory
Multiphase Flow CFD Simulation
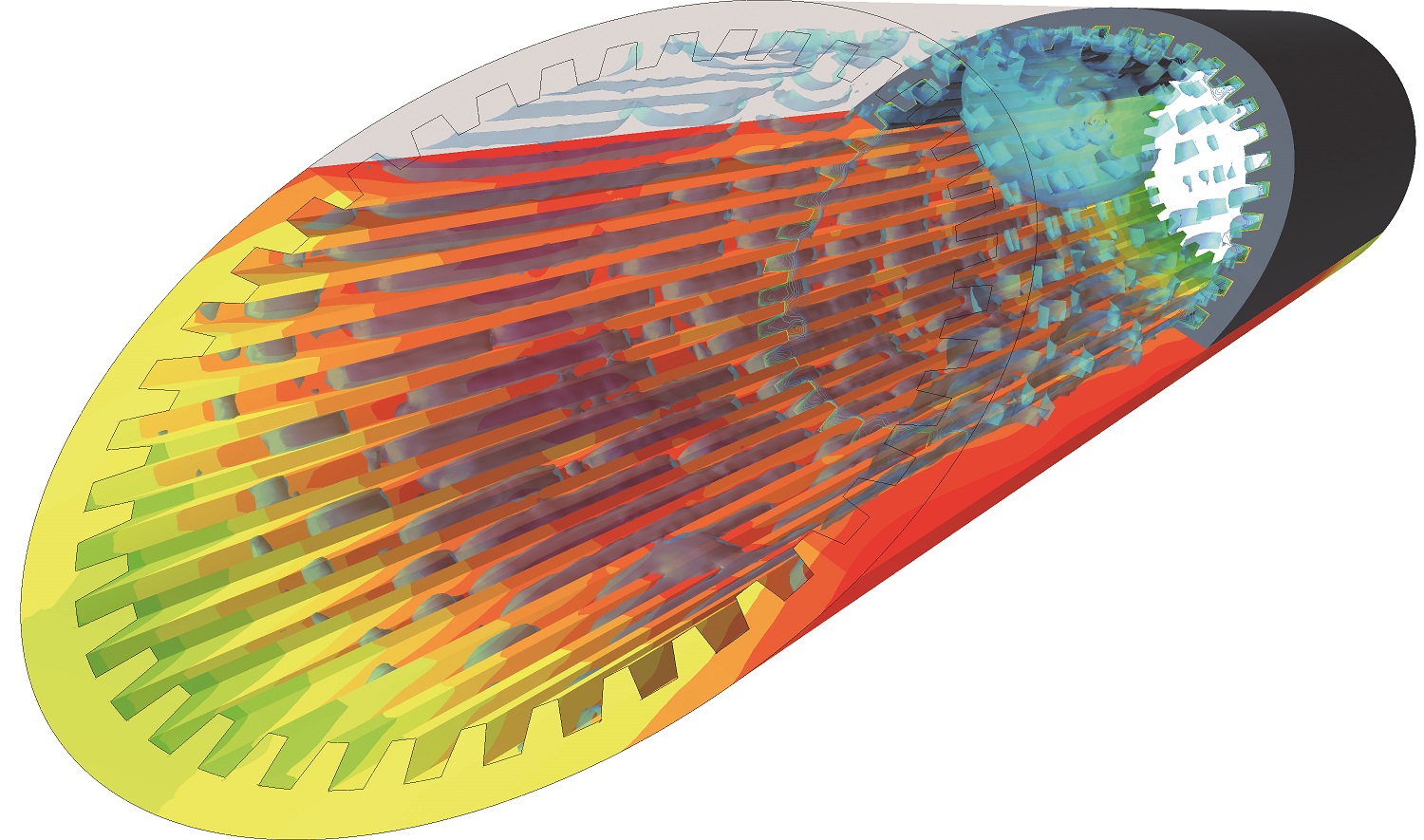
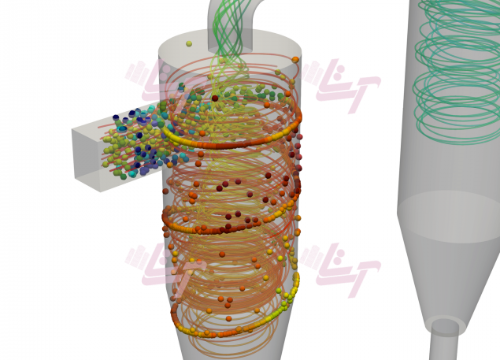
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is a popular method used for modeling systems utilizing single-phase flows and is widely used across industries for design optimization. However, their use in multiphase systems has been limited due to added complications of the two-phase interface with mass transfer causing complex flow behavior not easily predictable. CFD models are very promising in comparison to traditional techniques because they can predict detailed transient variations in individual phase velocities, void fractions and corresponding temperatures, not possible with other techniques. An accurate CFD model can not only address the flow transitions but also the corresponding heat transfer and pressure drop behaviors. Multiphase flows are very common in industrial applications. Therefore it is important to investigate them in detail to be able to predict the behavior of such systems and optimize them for best performance. Verified simulation tools and methods can provide a detailed insight at reasonable time and cost frame. Computational fluid dynamic (CFD) can give a full spatial and temporal representation of multiphase systems. Using CFD, different multiphase phenomena such as mass transfer, heat transfer, bubble or droplet breakup, coalescence etc in complex geometries can be investigated and interpreted to help improving the process.Detailed multiphase simulations (e.g. volume of fluid - VOF) can help for better understanding of the underlaying phenomena (heat and mass transfer) and developing closure models for being applied to less detailed multiphase simulation approaches (e.g. Euler-Euler) to be used for simulating big and complex geometries. To refine all the needed details in a multiphase simulation the discretization (mesh) should be fine enough to capture all the flow and the phase structures. Big geometries are usually simulated on multiple CPU cores in parallel to reduce the overall calculation time. However, by using a dynamic meshing the calculation load of each processor core varies during the time, since the details needing refinement.
View related Projects from this section